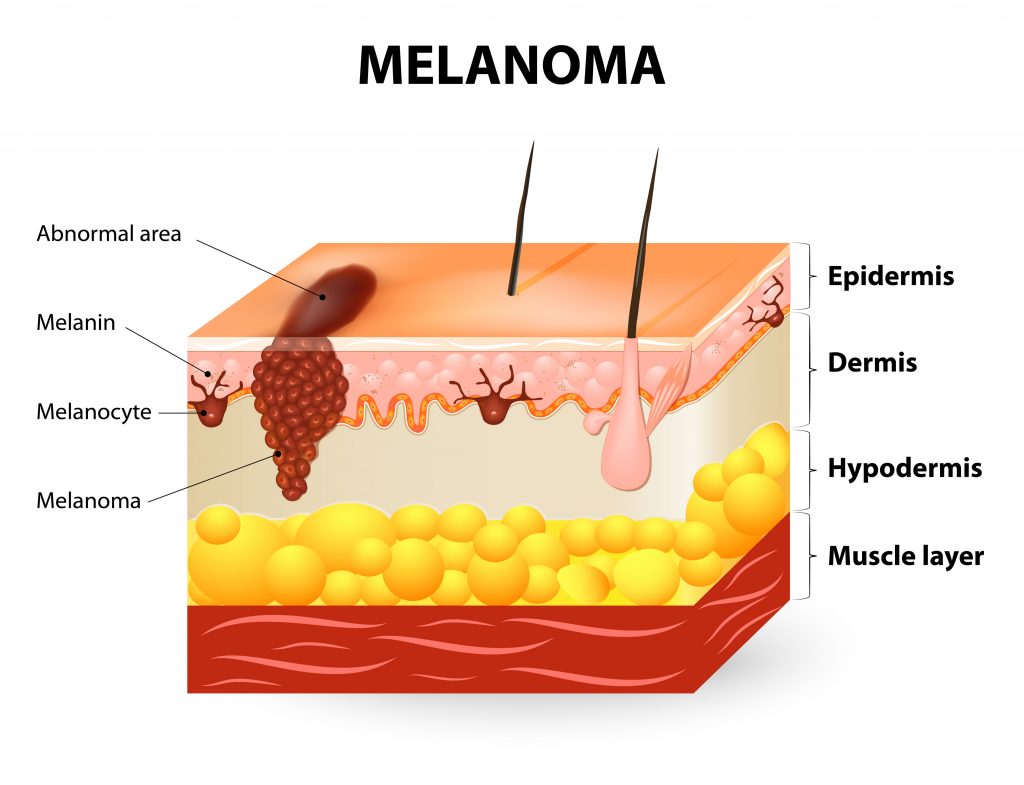
What is Nevus Mapping
Digital nevus mapping is the most important means of preventing and controlling skin nevi. The technology in the hands of a dermatologist specialised and experienced in dermoscopy (Dermoscopy Diploma, Medical University of Graz, Austria) enables the early diagnosis of melanoma at a very early stage. For this purpose, a high-resolution dermoscope is used, as well as polarized light, which makes it possible to “photograph” nevi in depth, with very high accuracy.
This examination allows the doctor to monitor and compare the nevi over time, observing in great detail any possible change.
What are the benefits of nevus mapping?
Digital nevus mapping is necessary in the following cases:
- When there is a history of melanoma
- When there are multiple nevi
- When there is a history of burns
- When there is a weakened immune system
How is the examination of nevi performed at the doctor’s office?
In the first visit, we examine the whole body of the patient, both with the naked eye and with a dermatoscope. In the case that we detect a lesion with melanoma characteristics, we proceed with its removal.
When there is no such lesion, we proceed to the digital imaging of nevi which includes two stages:
- The first stage includes the Whole Body Clinical Imaging. This procedure is very important as the technology makes it possible to compare with the clinical photos that will be taken in the following period in order to identify possible new lesions that were not present in previous visits
- Dermoscopic Imaging: In this phase we dermatoscopically record all nevi that are larger than two millimeters in diameter and register them topographically with the help of special software. It is this software that allows us to make a comparative assessment and note if the pattern of any nevi differ from others.
This assessment is based on the fact that nevi on the same person have a similar dermatoscopic pattern while melanoma has completely different characteristics that make it stand out.
In case that any damage is detected, our medical expert will decide whether it should be removed immediately or schedule an appointment for it to be rechecked after a short period of time.