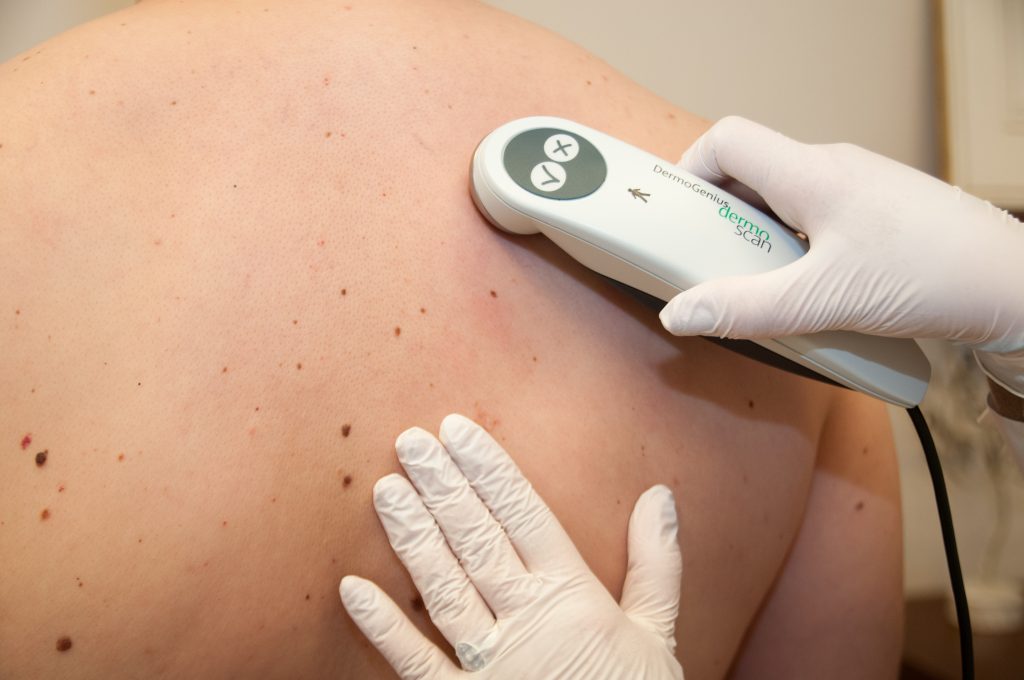
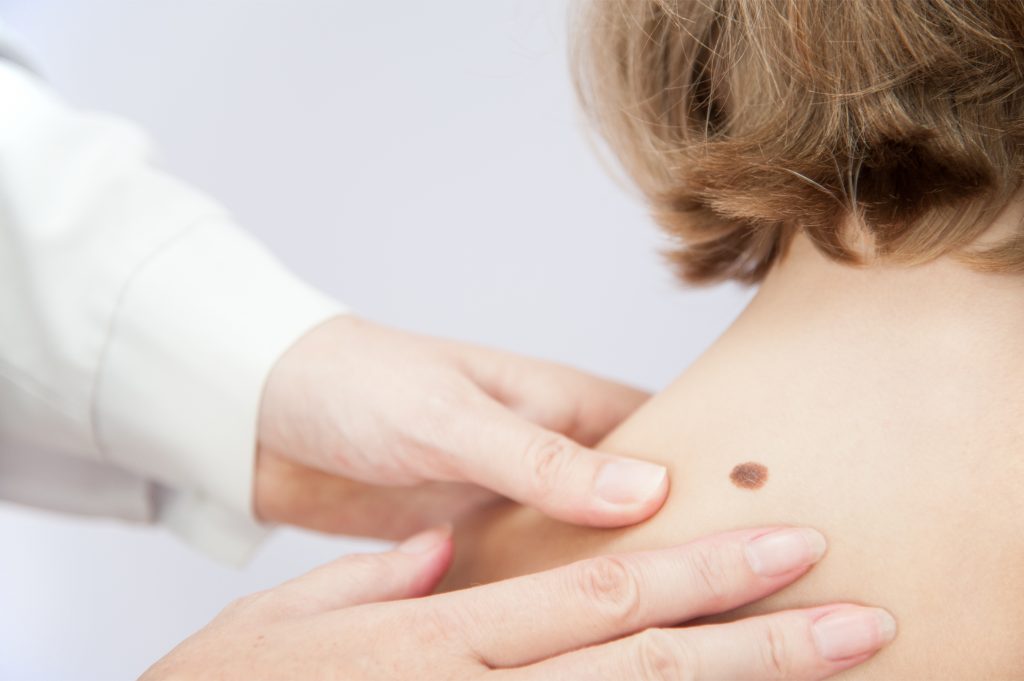
They are benign skin tumors, which are made up of spilocytes, a type of cell derived from melanocytes.
Congenital nevi are present from birth or develop during infancy. About 1% of newborns have at least one melanocytic nevus. Acquired nevi develop during childhood, up to the first years of adult life. Few nevi develop after the age of 35.
Radial Hyperkeratosis: They are hyperkeratotic lesions that can develop into malignant ones. They are a result of the long-term cumulative effect of solar radiation on keratinocytes.
The probability of occurrence after 40 increases with age and they are found in people with skin type I and II. The areas on the head most often affected are the face, ears, neck and hairline. Depending on the location and after some years, some can develop into squamous cell carcinoma.
Squamous cell carcinoma: It is a primary malignant neoplasm of the skin due to the mutation of the keratinocytes of the skin or mucous membranes.
It is found mainly on the head, neck and hands of elderly patients. It is the second most common skin cancer. Primary squamous cell carcinomas occur in sun-exposed areas and are due to the long-term damaging effect of radiation.
Basal cell carcinoma: It is the most common malignant neoplasm of the skinand causes local tissue destruction. It develops slowly.
It usually occurs after the age of 40 and more often in people with skin type I and II. It is associated with intermittent exposure (holiday, sunburn, childhood) of the patient to the sun and ionizing radiation.
It is a malignant neoplasm originating from melanocytes, the frequency of which is constantly increasing. It is usually found on the skin. Early diagnosis and treatment often lead to the healing of the damage.
It is the most common malignant disease in women aged 25-29 and the second most common after breast cancer in women aged 30-35.< /p>
Aggravating factors are:
- Light coloured skin
- Atypical nevi on protected and exposed skin areas
- History of melanoma
- Family history of atypical nevi or melanoma
- History of sunburn
- Congenital melanocytic nevi